WHAT IS BITCOIN: Bitcoin is a digital form of currency that operates on a decentralized network, meaning it isn’t controlled by any central authority like a government or a bank. It was introduced in 2009 by an anonymous individual or group of people using the name Satoshi Nakamoto. Bitcoin transactions are verified through a process called mining, where powerful computers solve complex mathematical puzzles to ensure the legitimacy of each transaction. These transactions are recorded on a public ledger known as the blockchain. Bitcoin can be used for online purchases or as an investment, and its value fluctuates based on market demand. It has gained attention for its potential to revolutionize the financial world, offering an alternative to traditional banking systems and providing users with more privacy and control over their money.
Who created Bitcoin and how
In 2008, Nakamoto published a whitepaper titled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System,” which outlined the principles of the new digital currency and its underlying technology, blockchain. The paper proposed a decentralized system for transferring value without relying on central authorities like banks or governments.
In 2009, Nakamoto released the first Bitcoin software, and the Bitcoin network went live when Nakamoto mined the first block, known as the genesis block or Block 0. This marked the beginning of Bitcoin’s existence. Nakamoto’s identity remains unknown, despite various theories and claims of having identified them, and Nakamoto gradually withdrew from public involvement in Bitcoin’s development by 2010. Since then, Bitcoin has been maintained and developed by a decentralized community of developers and miners.
Some interesting facts about Bitcoin
Here are some interesting facts about Bitcoin:
Bitcoin’s Resilience: Despite multiple challenges, including regulatory scrutiny, cyberattacks, and market crashes, Bitcoin has survived for over a decade and remains one of the most well-known and valuable cryptocurrencies in the world.
Limited Supply: Bitcoin has a fixed maximum supply of 21 million coins. This scarcity is one reason it’s often compared to gold, as the supply cannot be increased by any central authority or through inflation.
The First Bitcoin Transaction: The first-ever purchase using Bitcoin occurred in May 2010, when a programmer named Laszlo Hanyecz paid 10,000 Bitcoins for two pizzas. At the time, those coins were worth about $25 USD, but today they would be worth hundreds of millions of dollars.
Bitcoin Mining: New Bitcoins are created through a process called mining, where miners use powerful computers to solve complex mathematical problems. Over time, the reward decreases, making Bitcoin progressively more difficult to mine.
Bitcoin’s Creator Remains Unknown: Despite numerous attempts to uncover their identity, the true identity of Satoshi Nakamoto, the person or group who created Bitcoin, remains a mystery. Nakamoto communicated primarily through online forums and emails but gradually withdrew from the project by 2010.
Blockchain Technology: Bitcoin operates on blockchain technology, which is a decentralized ledger of all transactions ever made with Bitcoin. The blockchain is maintained by a global network of computers, making it nearly impossible to alter or counterfeit transactions.
Bitcoin’s Environmental Impact: Bitcoin mining uses a significant amount of energy, mainly due to the computational power needed to mine new coins. This has sparked debates about its environmental impact, with some arguing that Bitcoin mining contributes to increased carbon emissions.
Price Volatility: Bitcoin is known for its extreme price volatility. Its value can fluctuate dramatically within short periods, making it both a high-risk investment and a potential hedge against inflation for some investors.
First Country to Adopt Bitcoin as Legal Tender: In 2021, El Salvador became the first country to officially adopt Bitcoin as legal tender, allowing it to be used alongside the U.S. dollar for transactions.
Bitcoin and Privacy: While Bitcoin transactions are visible on the public blockchain, they are pseudonymous. This means that while the transaction details are open, the identities behind Bitcoin addresses remain anonymous unless revealed through other means.
What are the benefits of bitcoin
Bitcoin offers several benefits, particularly in the realms of finance and technology. Here are some key advantages:
- Decentralization: Bitcoin operates on a decentralized network, meaning there is no central authority like a bank or government controlling it. This gives users more control over their money and transactions, free from external influence or restrictions.
- Lower Transaction Fees: Bitcoin transactions typically have lower fees compared to traditional banking systems, especially for cross-border transactions. This is particularly beneficial for people sending money internationally.
- Fast and Global Transactions: Bitcoin transactions can be completed in minutes, regardless of geographical location. This makes it ideal for international payments, as users do not need to wait for traditional banking processes, which can take several days.
- Security and Transparency: Bitcoin uses blockchain technology, which provides a high level of security and transparency. Each transaction is recorded in a public ledger, making it difficult to alter or counterfeit transactions. This decentralized ledger is also nearly tamper-proof.
- Inflation Hedge: With a capped supply of 21 million coins, Bitcoin is often seen as a store of value that can protect against inflation. Unlike fiat currencies, which can be printed by governments and lose value over time, Bitcoin’s limited supply makes it more resilient to inflationary pressures.
- Financial Inclusion: Bitcoin provides financial services to people without access to traditional banking systems. All that is needed is an internet connection, allowing individuals in remote or underbanked regions to send, receive, and store money securely.
- Privacy and Pseudonymity: Bitcoin transactions are pseudonymous, meaning that while the transaction details are publicly visible, the identities of users behind Bitcoin addresses are not directly tied to real-world identities. This can offer more privacy compared to traditional banking.
- Ownership and Control: Bitcoin gives users full ownership and control over their funds. Unlike traditional banking, where third-party institutions hold and manage your money, Bitcoin allows individuals to store their wealth in their own wallets, reducing reliance on intermediaries.
- Potential for High Returns: Due to its volatility, Bitcoin has offered significant returns for early investors and traders. While it’s a high-risk investment, its price has seen massive growth since its inception, attracting both retail and institutional investors.
- Innovation and Technology: Bitcoin is a pioneer in blockchain technology, which has led to the development of various other cryptocurrencies and blockchain-based applications. Its innovation has sparked a global movement towards decentralized finance (DeFi) and digital assets.
These benefits make Bitcoin an attractive alternative to traditional financial systems for many people, although it is important to recognize the risks, such as its price volatility and regulatory uncertainties.
What are the disadvantages of bitcoin
While Bitcoin offers several benefits, it also has some significant disadvantages. Here are some of the key drawbacks:
- Price Volatility: Its value can fluctuate dramatically in a short period of time, making it a risky investment. This volatility can be problematic for users who wish to use Bitcoin as a stable store of value or a medium of exchange.
- Scalability Issues: Bitcoin’s network has limited transaction processing capacity, which can lead to slower transaction times and higher fees during times of high demand. This scalability issue makes Bitcoin less practical for everyday transactions compared to traditional payment systems like Visa or Mastercard.
- Environmental Impact: Bitcoin mining requires a vast amount of computational power, leading to significant energy consumption. This has raised concerns about the environmental impact, especially in regions where energy is generated from non-renewable sources. The carbon footprint of Bitcoin mining is a topic of ongoing debate.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Bitcoin operates in a relatively unclear legal and regulatory environment. Different countries have varying attitudes toward Bitcoin, ranging from acceptance to outright bans. This uncertainty can cause instability in its value and could pose legal risks for users and businesses.
- Security Risks: While Bitcoin’s blockchain is highly secure, users must take extra precautions to protect their private keys (which are needed to access their Bitcoin). If a user loses their private key or is hacked, they could lose access to their Bitcoin permanently. Unlike traditional bank accounts, there is no way to recover lost or stolen Bitcoin.
- Limited Acceptance: While Bitcoin is gaining popularity, it is still not widely accepted by merchants and businesses for everyday transactions. The relatively low adoption of Bitcoin for regular purchases limits its use as a practical currency for most people.
- Lack of Consumer Protections: Bitcoin transactions are irreversible. Once a transaction is confirmed, it cannot be undone, which leaves no room for recourse in cases of fraud or mistakes. Traditional financial systems offer some protection against fraudulent charges, but Bitcoin does not.
- Complexity for Beginners: Bitcoin and the underlying blockchain technology can be difficult for beginners to understand and use. Setting up a wallet, securing private keys, and managing transactions can be challenging, which may deter some users from adopting Bitcoin.
- Risk of Illegal Activities: Due to its pseudonymous nature, Bitcoin has been associated with illegal activities, such as money laundering, tax evasion, and purchasing illicit goods on the dark web. This association has led to negative perceptions of Bitcoin, despite its legitimate uses.
- Market Manipulation: Bitcoin’s market can be susceptible to manipulation by large holders of the currency (often referred to as “whales”). These large entities can influence Bitcoin’s price by making large trades or by using other tactics to sway market sentiment, which can create artificial price swings.
These disadvantages highlight the challenges of using and investing in Bitcoin, particularly for those who are new to the cryptocurrency space or those looking for stability and predictability in their financial transactions.
What is the history of bitcoin
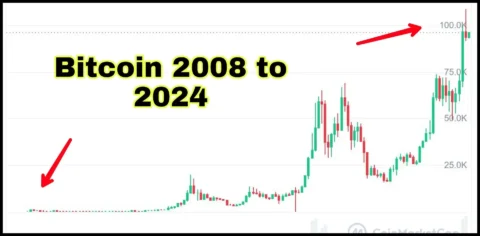
The history of Bitcoin is a fascinating journey that began with an idea for a decentralized digital currency and has since transformed into a global phenomenon. Here’s an overview of Bitcoin’s history:
1. The Concept (2008)
- In 2008, an anonymous person or group of people using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto published a whitepaper titled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System.” This paper introduced the concept of Bitcoin as a decentralized digital currency that would operate without the need for intermediaries like banks or governments.
- The goal was to create a currency that could allow for secure, low-cost, and borderless transactions, which would be enabled by blockchain technology — a distributed ledger that records all transactions in a secure, transparent manner.
2. Bitcoin’s Genesis Block (2009)
- January 3, 2009, marked the launch of Bitcoin when Nakamoto mined the genesis block (the first block on the Bitcoin blockchain). This block contained a reward of 50 Bitcoins, and it included a hidden message: “The Times 03/Jan/2009 Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks”. This message was widely interpreted as a critique of traditional financial systems and the banking crisis at the time.
- The first-ever Bitcoin transaction took place shortly after, when Nakamoto sent 10 Bitcoins to a computer scientist named Hal Finney.
3. Bitcoin’s Early Days (2009-2010)
- Bitcoin software was released in 2009, allowing others to start mining and using Bitcoin. During this period, Bitcoin had little to no value, and it was mainly exchanged among early adopters.
- May 22, 2010, is remembered as Bitcoin Pizza Day, when a programmer named Laszlo Hanyecz paid 10,000 Bitcoins for two pizzas. At the time, those 10,000 Bitcoins were worth about $25 USD. Today, that amount of Bitcoin would be worth millions of dollars.
- By late 2010, Bitcoin had reached a value of $1 per Bitcoin for the first time, thanks to increasing interest from users and small businesses.
4. Growth and Early Speculation (2011-2013)
- In 2011, Bitcoin began to gain more attention as it was listed on more exchanges. Bitcoin’s value rose to $1 for the first time in February 2011, which was a milestone for the cryptocurrency.
- The price reached $31 by mid-2011, but it quickly fell, highlighting Bitcoin’s volatility.
- In 2013, Bitcoin made headlines again when its price surged to $266 in April, then dropped significantly. This volatility became a characteristic of Bitcoin’s price movements.
- Bitcoin also gained notoriety for its association with the Silk Road, an online marketplace where users could purchase illicit goods using Bitcoin. This raised concerns among governments and regulators.
5. Increasing Popularity and Regulation (2014-2017)
- In 2014, large companies like Overstock.com and Newegg began accepting Bitcoin as payment, marking the first steps toward mainstream adoption.
- Coinbase, a digital wallet and exchange platform, was founded in 2012, providing a more user-friendly interface for buying and selling Bitcoin.
- In 2013, Bitcoin’s price surged again, reaching a new high of $1,000 before falling back down. Despite the volatility, Bitcoin gained attention from investors and regulators.
- In 2014, Mt. Gox, one of the largest Bitcoin exchanges at the time, was hacked, resulting in the loss of 850,000 Bitcoins. This incident highlighted the need for better security in the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
- In 2017, Bitcoin reached an all-time high of nearly $20,000 per Bitcoin during a massive rally, driven by increased mainstream media attention and speculation.
6. The Rise of Altcoins and Market Maturation (2017-2020)
- As Bitcoin’s popularity grew, many other cryptocurrencies (known as altcoins) were launched, including Ethereum, Ripple (XRP), and Litecoin. This helped to further legitimize the cryptocurrency space.
- The cryptocurrency market went through a bubble in late 2017, which burst in early 2018, leading to a major price correction. Bitcoin’s price fell dramatically, but it still remained much higher than its early days.
- During the next few years, Bitcoin’s price remained relatively stable, although it saw occasional surges and corrections. The launch of Bitcoin futures trading in 2017 on major exchanges like the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) helped to further establish Bitcoin as a legitimate asset.
- Bitcoin scaling debates took place in 2017, leading to the creation of Bitcoin Cash (BCH), a fork of Bitcoin designed to handle more transactions by increasing the block size limit.
7. Institutional Adoption and New Record Highs (2020-Present)
- 2020 marked a turning point for Bitcoin, as institutional investors and large corporations began to take notice. Companies like MicroStrategy and Tesla invested billions of dollars into Bitcoin, seeing it as a hedge against inflation and economic uncertainty.
- In 2020, Bitcoin experienced a major rally, with its price crossing $20,000 again. By 2021, Bitcoin reached a new all-time high of over $64,000 before experiencing some volatility.
- The rise of decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, the integration of Bitcoin into payment platforms like PayPal and Square, and the launch of Bitcoin ETFs (exchange-traded funds) further cemented Bitcoin’s place in the global financial system.
- El Salvador made history in 2021 by becoming the first country to officially adopt Bitcoin as legal tender, allowing it to be used alongside the U.S. dollar for transactions.
8. Bitcoin Today
- As of 2024, Bitcoin continues to be a dominant force in the world of cryptocurrencies, often seen as “digital gold” due to its limited supply and growing institutional adoption.
- Bitcoin’s value remains volatile, but it is increasingly viewed as a store of value, especially by hedge funds, corporations, and even some governments. It’s used for remittances, investment, and as a hedge against inflation.
- Bitcoin’s ongoing development includes efforts to improve scalability, such as the Lightning Network, which aims to enable faster and cheaper transactions on top of the Bitcoin blockchain.
Key Events in Bitcoin’s History:
- 2008: Satoshi Nakamoto releases the Bitcoin whitepaper.
- 2009: The first Bitcoin block (genesis block) is mined.
- 2010: The first Bitcoin transaction (10,000 BTC for pizza).
- 2011: Bitcoin hits $1.
- 2013: Bitcoin reaches $1,000, and the Silk Road is shut down.
- 2017: Bitcoin hits an all-time high of nearly $20,000.
- 2020: Institutional adoption rises; Bitcoin’s price surges past $20,000.
- 2021: El Salvador adopts Bitcoin as legal tender; Bitcoin hits $64,000.
Bitcoin’s history has been marked by innovation, volatility, and regulatory challenges. From its humble beginnings as an idea proposed by an anonymous creator to its current status as a globally recognized digital asset, Bitcoin has dramatically altered the landscape of finance, paving the way for the broader adoption of blockchain and cryptocurrency technologies.
Ways to earn money from Bitcoin
There are several ways to earn money from Bitcoin, each with its own level of risk and effort required. Here are some popular methods:
1. Buying and Holding (HODLing)
- What it is: This involves buying Bitcoin and holding onto it for a long period, hoping that its value will increase over time. Investors sell their Bitcoin at a higher price to make a profit.
- How to earn: You earn money by buying Bitcoin at a low price and selling it when the price rises. This method requires patience and a long-term outlook on Bitcoin’s potential for growth.
- Risk: The price of Bitcoin is highly volatile, so the value of your investment can fluctuate significantly.
2. Bitcoin Trading
- What it is: Bitcoin trading involves buying and selling Bitcoin frequently to take advantage of price fluctuations. Traders use different strategies, including day trading, swing trading, and arbitrage.
- How to earn: By buying Bitcoin at a low price and selling it at a higher price in a short time frame, traders can earn profits. Some traders also use leverage to amplify their gains (and potential losses).
- Risk: Trading can be risky due to Bitcoin’s price volatility. It requires expertise and market knowledge to be successful.
3. Bitcoin Mining
- What it is: Bitcoin mining involves using powerful computers to solve complex mathematical problems that validate transactions on the Bitcoin network. Miners are rewarded with newly created Bitcoin.
- How to earn: Miners earn Bitcoin as a reward for contributing computational power to the network. The more computational power you contribute, the higher your chances of earning Bitcoin.
- Risk: Mining requires significant investment in specialized hardware and consumes a lot of electricity. It’s also competitive, with the potential for diminishing returns as mining difficulty increases over time.
4. Staking and Yield Farming (for Other Cryptocurrencies)
- What it is: While Bitcoin itself doesn’t use staking, some other cryptocurrencies that operate on proof-of-stake blockchains allow users to “stake” their coins and earn rewards. Yield farming involves lending out cryptocurrencies in decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols to earn interest.
- How to earn: You can earn passive income by staking your Bitcoin or lending it out to earn interest through platforms that offer such services. Note that many of these services involve converting Bitcoin into other cryptocurrencies.
- Risk: These methods may involve using third-party platforms, which can carry risks such as hacking, platform failure, or regulatory issues.
5. Earn Bitcoin through Freelance Work
- What it is: Many freelancers accept Bitcoin as payment for their services. Websites like Bitwage allow workers to receive their salary in Bitcoin, or freelancers can directly ask clients to pay in Bitcoin.
- How to earn: If you have skills like writing, graphic design, programming, or consulting, you can offer your services and accept Bitcoin as payment.
- Risk: Payments in Bitcoin are irreversible, so you need to ensure that both parties agree on terms to avoid potential disputes.
6. Bitcoin Faucets
- What it is: Bitcoin faucets are websites that give away small amounts of Bitcoin for free in exchange for completing simple tasks like solving captchas, viewing ads, or engaging with the site in other ways.
- How to earn: By visiting a Bitcoin faucet and completing the required tasks, you can earn small amounts of Bitcoin over time.
- Risk: The rewards are usually very small, and it may take a long time to accumulate a significant amount of Bitcoin.
7. Affiliate Programs
- What it is: Many Bitcoin-related platforms, such as exchanges and wallets, offer affiliate programs where you can earn Bitcoin by referring new users to their platform.
- How to earn: By promoting a Bitcoin exchange, wallet, or service, you earn commissions in Bitcoin when someone signs up through your referral link and completes certain actions (like making a trade or deposit).
- Risk: The income from affiliate programs depends on how successful your marketing efforts are. You also need to trust the platform’s reliability.
8. Bitcoin Lending
- What it is: Bitcoin lending platforms allow you to lend your Bitcoin to others in exchange for interest payments. This can be done through platforms such as BlockFi or Nexo.
- How to earn: By lending your Bitcoin, you receive interest on your loan. These platforms generally offer higher returns than traditional savings accounts.
- Risk: Lending involves the risk of default or platform failure. You should be aware of the risks and ensure the platform has proper security measures in place.
9. Accept Bitcoin as Payment
- What it is: If you own a business or provide services, you can start accepting Bitcoin as payment for your goods or services.
- How to earn: You can directly earn Bitcoin by offering your products or services and allowing customers to pay with Bitcoin.
- Risk: The price of Bitcoin can fluctuate, so it’s important to decide whether you’ll hold the Bitcoin as an investment or convert it into fiat currency immediately.
10. Bitcoin Airdrops and Forks
- What it is: Sometimes, Bitcoin-based projects distribute free tokens or coins to Bitcoin holders (called an airdrop), or a blockchain can undergo a hard fork, creating a new cryptocurrency.
- How to earn: By holding Bitcoin, you might be eligible to receive free tokens from projects or get free coins in the event of a hard fork.
- Risk: Airdrops and forks often involve unknown or risky projects, and there may be scams or tax implications to consider.
These methods offer different levels of risk, effort, and reward. Whether you’re looking to earn passive income, trade actively, or invest for the long term, Bitcoin presents numerous opportunities to earn money. However, each method carries its own risks, so it’s important to research thoroughly and ensure you’re comfortable with the associated risks before getting started.
How to invest in bitcoin
Investing in Bitcoin can be an exciting and potentially profitable venture, but it also involves risks due to its price volatility.
1. Set Your Investment Goals
- Decide on your investment strategy: Are you looking to invest for the long-term (HODLing), or do you plan to actively trade Bitcoin to take advantage of market fluctuations? Setting clear goals will help guide your approach.
- Determine how much to invest: Only invest what you are willing to lose, as Bitcoin can be very volatile. Many investors start with a small portion of their portfolio and increase it over time as they gain confidence and experience.
2. Choose a Reliable Bitcoin Exchange
- Select a platform: Choose a trustworthy cryptocurrency exchange where you can buy, sell, and store Bitcoin. Some popular exchanges include:
- Coinbase
- Binance
- Kraken
- Gemini
- eToro
- Consider factors: Look for an exchange that offers low fees, good customer support, ease of use, and strong security features. Be sure the exchange operates in your country and complies with local regulations.

3. Create an Account
- Sign up: Register for an account on your chosen exchange. You’ll need to provide your email address, create a password, and verify your identity with KYC (Know Your Customer) procedures. This may require uploading a government-issued ID and proof of address.
- Set up two-factor authentication (2FA): For added security, enable 2FA to protect your account from unauthorized access.
4. Deposit Funds
- Deposit fiat currency: Most exchanges allow you to deposit money using bank transfers, credit/debit cards, or PayPal (depending on the exchange). Bank transfers typically have lower fees, but they can take longer to process.
- Use cryptocurrency: If you already own other cryptocurrencies, you can deposit them directly to the exchange to trade for Bitcoin.
5. Buy Bitcoin
- Place a buy order: Once your funds are deposited, you can place an order to buy Bitcoin. There are typically two types of orders:
- Market order: Buy Bitcoin at the current market price. This is the simplest and quickest option.
- Limit order: Set a specific price at which you want to buy Bitcoin. Your order will only be executed if the price reaches that level.
- Choose the amount: Decide how much Bitcoin you want to buy. You can buy fractional Bitcoin (e.g., 0.01 BTC), as Bitcoin is divisible into smaller units.
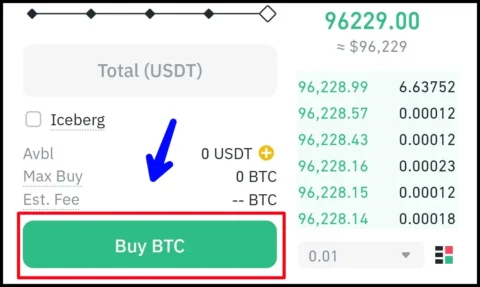
6. Store Your Bitcoin Safely
- Wallet options: Once you’ve purchased Bitcoin, it’s essential to store it securely. You can keep your Bitcoin in two types of wallets:
- Exchange wallet: Some exchanges provide wallets where you can store your Bitcoin, but they are more vulnerable to hacks and theft. Use this option for short-term holding or trading.
- Private wallet: For added security, consider using a private cryptocurrency wallet. There are two types:
- Hot wallets: These are software wallets connected to the internet, such as Exodus or Electrum. They are convenient for quick access to Bitcoin but are more susceptible to online threats.
- Cold wallets: These are hardware wallets, like Ledger Nano S or Trezor, which store your Bitcoin offline and are much more secure against hacks. Cold storage is ideal for long-term holding.

7. Monitor the Market
- Track Bitcoin prices: Use price tracking apps or the exchange’s interface to keep an eye on Bitcoin’s price. Cryptocurrency prices can fluctuate rapidly, so it’s important to stay informed about market trends.
- Set alerts: Some exchanges and apps allow you to set price alerts, so you are notified when Bitcoin reaches a certain value.
8. Consider Dollar-Cost Averaging (DCA)
- What is DCA?: Dollar-cost averaging involves investing a fixed amount in Bitcoin at regular intervals (e.g., weekly or monthly), regardless of the price. This strategy helps reduce the impact of short-term price volatility and lowers the risk of making poor timing decisions.
9. Stay Informed
- Stay updated: Follow news related to Bitcoin and the broader cryptocurrency market. Regulatory changes, technological advancements, and macroeconomic factors can all impact Bitcoin’s price.
- Join communities: Participate in online forums and communities (such as Reddit, Twitter, or Bitcoin-specific groups) to learn more from experienced investors.
10. Tax Considerations
- Understand tax implications: In many countries, Bitcoin is subject to taxes, such as capital gains tax when sold for a profit. Be aware of your country’s tax laws and keep detailed records of all your transactions for tax reporting purposes.
- Consult a tax professional: If you’re unsure about how to report your Bitcoin holdings and transactions, it’s a good idea to consult a tax professional who is familiar with cryptocurrency.
Risks of Investing in Bitcoin:
- Price volatility: Bitcoin’s price can change dramatically, which may result in significant gains or losses.
- Regulatory risk: Bitcoin faces regulatory uncertainty in many countries, which could impact its price and availability.
- Security risks: While Bitcoin’s network is secure, there is still a risk of hacking, especially if you don’t use proper security measures like cold storage.
By following these steps and understanding the associated risks, you can begin investing in Bitcoin. It’s crucial to educate yourself about Bitcoin’s potential and challenges and approach your investment with caution, especially given the volatility and evolving nature of the cryptocurrency market.
FAQs –
Q 1. How much money can you invest in bitcoin
Answer – You can invest any amount in Bitcoin, even as little as a few dollars, since Bitcoin is divisible into small units called satoshis. The minimum investment is typically determined by the exchange you use, but you can start with as little as $1 or $10, depending on your preference.
Q 2. How high will the price of Bitcoin go? What is the prediction?
Answer – The future price of Bitcoin is highly uncertain and depends on various factors like market demand, regulatory developments, and adoption. Predictions vary widely, with some experts suggesting it could reach $100,000 or more in the next few years, while others warn it could experience significant declines due to volatility. It’s important to remember that Bitcoin is speculative, and no one can predict its price with certainty.
Q 3. Who can invest in Bitcoin
Answer – Anyone with access to a cryptocurrency exchange and the necessary funds can invest in Bitcoin. This includes individuals, institutions, and even businesses. However, investors must be of legal age in their country and comply with local regulations.
Q 4. What is the minimum age to invest in Bitcoin?
Answer – The minimum age to invest in Bitcoin is typically 18 years old. However, the exact age requirement can vary depending on the country and the cryptocurrency exchange you use. Some platforms may allow individuals under 18 to invest with parental consent or through custodial accounts. Always check the specific exchange’s terms and conditions.
Conclusion –
In conclusion, Bitcoin has revolutionized the financial world by offering a decentralized, digital alternative to traditional currencies. Its history, marked by significant milestones, showcases its evolution from an experimental concept to a global asset class. Despite its volatility and regulatory challenges, Bitcoin continues to attract investors and institutions, being seen as a potential hedge against inflation and a store of value. As blockchain technology matures and adoption grows, Bitcoin’s future remains uncertain, yet it undeniably plays a pivotal role in shaping the future of finance. Whether you view it as a speculative investment or a groundbreaking innovation, Bitcoin’s impact is undeniable, and its journey is far from over.