WHAT IS ETHEREUM IN CRYPTO: Ethereum Coin, commonly referred to as Ether (ETH), is the native cryptocurrency of the Ethereum blockchain. It is used to power the network by paying for transaction fees, computational services, and executing smart contracts. Unlike Bitcoin, which primarily functions as a digital currency, Ether has a broader role within the Ethereum ecosystem.
It is essential for interacting with decentralized applications (dApps) and for incentivizing participants to secure the network through mining or staking (in Ethereum 2.0). Ether’s value fluctuates based on demand for network usage and its role in the growing decentralized finance (DeFi) sector.
It is the second-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization after Bitcoin, and its utility extends beyond just a store of value, powering the decentralized internet and smart contract platforms.
Interesting information about Ethereum
Here are some interesting and lesser-known facts about Ethereum (ETH) that highlight its significance and innovation in the crypto world:
- More than Just a Cryptocurrency: While Ethereum Coin (ETH) is widely recognized as a cryptocurrency, it serves a much broader purpose. Ethereum powers an entire ecosystem of decentralized applications (dApps), smart contracts, and decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, making it a cornerstone of the blockchain space.
- Smart Contract Innovation: This innovation allows for trustless, automated transactions without intermediaries, revolutionizing industries like finance, real estate, and legal services.
- Ethereum 2.0 Transition: Ethereum is undergoing a major upgrade from its original proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanism to proof-of-stake (PoS), known as Ethereum 2.0. This transition aims to make the network more energy-efficient, faster, and scalable, potentially allowing it to process thousands of transactions per second (TPS) and dramatically reduce its carbon footprint.
- Gas Fees: Ethereum uses “gas” as a unit of measurement for transaction costs. Gas is required to pay for computational work done on the network, such as executing smart contracts or transferring Ether. These fees fluctuate depending on network congestion, which can sometimes lead to high fees during periods of heavy demand.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Ethereum is at the heart of the DeFi movement, which aims to recreate traditional financial services (like lending, borrowing, and trading) in a decentralized way, without relying on banks or other centralized authorities. The majority of DeFi projects and protocols run on the Ethereum network, driving demand for ETH.
- ERC-20 Tokens: Ethereum’s ability to create new tokens has led to the creation of thousands of different cryptocurrencies that are built on the Ethereum blockchain. These tokens, such as USDT (Tether), LINK (Chainlink), and UNI (Uniswap), follow the ERC-20 standard, allowing them to be easily exchanged and integrated within the Ethereum ecosystem.
- The DAO Hack and Hard Fork: In 2016, a major hack of a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) built on Ethereum led to a controversial hard fork. To reverse the effects of the hack, the Ethereum community decided to split the blockchain into two: Ethereum (ETH) and Ethereum Classic (ETC), with ETC being the original chain that did not reverse the hack.
- Ethereum’s Role in NFTs: Ethereum is the primary blockchain used for creating and trading non-fungible tokens (NFTs). These unique digital assets, representing anything from art to virtual land, rely on Ethereum’s standards (e.g., ERC-721 and ERC-1155) for their creation and transfer.
- Vitalik Buterin’s Vision: Ethereum’s creator, Vitalik Buterin, was just 19 years old when he proposed the Ethereum whitepaper in late 2013. He wanted to create a blockchain that went beyond digital currency to enable decentralized applications, which is now one of the most transformative concepts in the blockchain space.
- Staking Rewards: With Ethereum 2.0, ETH holders can participate in staking by locking up their Ether to help secure the network under the new PoS consensus model. In exchange, they earn rewards, making Ethereum a way for users to passively earn income by supporting the network’s operation.
These features make Ethereum not just a cryptocurrency, but a powerful platform driving innovation across various sectors, from finance to digital art, and positioning it as a foundational layer for Web3, the decentralized internet.
Here’s a table summarizing key information about Ethereum Coin (ETH):
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Name | Ethereum Coin (ETH) |
| Launch | July 30, 2015 |
| Creator | Vitalik Buterin and co-founders (Gavin Wood, Joseph Lubin, etc.) |
| Blockchain | open-source blockchain |
| Primary Use | Powering smart contracts, decentralized applications (dApps), and DeFi |
| Consensus Mechanism | Transitioning from Proof-of-Work (PoW) to Proof-of-Stake (PoS) under Ethereum 2.0 |
| Transaction Fees | Paid in “gas”, which are required for transactions and smart contract execution |
| Native Cryptocurrency | Ether (ETH) |
| Max Supply | No fixed supply (ETH is inflationary with an annual issuance, though Ethereum 2.0 will decrease inflation rate) |
| Current Supply | Over 120 million ETH (as of 2025, supply continues to grow) |
| Market Rank | 2nd largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization (after Bitcoin) |
| Use Cases | Smart contracts, dApps, DeFi, NFTs, staking rewards, token creation (ERC-20) |
| Ethereum 2.0 Upgrade | Transitioning to Proof-of-Stake for improved scalability, security, and energy efficiency |
| Major Events | DAO hack and hard fork (2016) resulting in Ethereum Classic (ETC) |
| Popular Tokens Built on ETH | USDT (Tether), LINK (Chainlink), UNI (Uniswap), DAI, and more ERC-20 tokens |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced energy consumption under Proof-of-Stake (ETH 2.0) |
| Staking | ETH holders can earn rewards by staking ETH in Ethereum 2.0’s PoS mechanism |
| Smart Contract Standard | ERC-20 (fungible tokens), ERC-721 and ERC-1155 (non-fungible tokens, NFTs) |
Advantages and disadvantages of Ethereum
Here are the advantages and disadvantages of Ethereum Coin (ETH) in the cryptocurrency ecosystem:

Advantages of Ethereum Coin (ETH)
- Smart Contracts and dApps: Ethereum enables the creation of decentralized applications (dApps) and self-executing smart contracts. This allows for automation of complex processes without intermediaries, improving efficiency, transparency, and security.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Ethereum is the backbone of the rapidly growing DeFi sector. It allows users to participate in decentralized financial activities like lending, borrowing, staking, and trading without relying on traditional financial institutions.
- Large Ecosystem: Ethereum has the largest developer community in the blockchain space. Its wide adoption has led to thousands of projects and tokens built on its platform, making it a robust and versatile network for innovation.
- ERC-20 Token Standard: Ethereum’s ERC-20 token standard has become the foundation for creating a wide range of new tokens. This has contributed to the growth of ICOs, DeFi platforms, and various other token-based projects.
- Ethereum 2.0 Upgrade: The ongoing transition to Ethereum 2.0 (from Proof-of-Work to Proof-of-Stake) promises to significantly improve scalability, reduce energy consumption, and enhance the network’s overall performance, making it more sustainable in the long run.
- Liquidity and Market Adoption: Ether (ETH) is widely recognized and has strong liquidity, meaning it can be easily traded across most cryptocurrency exchanges. It’s often used as collateral in decentralized lending platforms and as a reserve asset.
- Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): Ethereum is the primary blockchain for NFTs (non-fungible tokens), which have revolutionized digital art, collectibles, and gaming. This has brought Ethereum increased attention and adoption.
Disadvantages of Ethereum Coin (ETH)
- High Gas Fees: Ethereum has faced issues with high transaction fees (gas fees), especially during times of network congestion. This can make using Ethereum for small transactions expensive and less practical for everyday use.
- Scalability Issues: Although Ethereum 2.0 aims to address this, Ethereum has struggled with scalability. The network can become congested when there are high transaction volumes, leading to delays and high fees. This has limited its ability to handle a large number of transactions per second.
- Environmental Impact (Pre-Ethereum 2.0): Prior to Ethereum 2.0, Ethereum’s Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism was criticized for its energy consumption, which was similar to Bitcoin’s. Ethereum 2.0’s transition to Proof-of-Stake (PoS) is intended to resolve this concern, but the legacy issues still linger.
- Complexity for New Users: While Ethereum enables powerful features, its ecosystem can be complex for newcomers. Managing gas fees, understanding smart contracts, and interacting with dApps can be intimidating for those unfamiliar with blockchain technology.
- Security Vulnerabilities: Despite Ethereum’s decentralized nature, the platform has experienced vulnerabilities in its smart contracts and dApps. High-profile hacks, such as the DAO hack, exposed potential flaws in contract code and governance models, although the Ethereum community responded by implementing a hard fork.
- Competition: Ethereum faces increasing competition from other smart contract platforms like Binance Smart Chain, Cardano, and Solana, which offer faster transactions and lower fees. As these competitors grow, Ethereum may lose market share.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: As with other cryptocurrencies, Ethereum faces ongoing regulatory scrutiny. The legal landscape surrounding Ethereum and decentralized platforms is still evolving, and potential future regulations could impact its use and value.
History of Ethereum Coin in Crypto
The history of Ethereum Coin (ETH) in the cryptocurrency space is marked by innovation, growth, and significant milestones that have shaped the blockchain and cryptocurrency landscape. Here’s an overview of the key events in Ethereum’s history:
1. Early Concept and Creation (2013-2014)
- 2013: The idea for Ethereum was proposed by Vitalik Buterin, a young programmer and researcher, who was inspired by the limitations of Bitcoin. He envisioned a blockchain not just for digital currency but also for supporting decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts, which would allow for automated, self-executing contracts without intermediaries.
- Late 2013: Buterin released the Ethereum whitepaper, outlining the technical details and vision for Ethereum. The idea quickly gained attention from developers and cryptographers, leading to the formation of the Ethereum project.
- Early 2014: Buterin, along with co-founders Gavin Wood, Joseph Lubin, and others, officially launched the Ethereum project. They began gathering funds for the project through an initial coin offering (ICO), which would become one of the first successful ICOs in the crypto space.
2. Ethereum’s ICO and Launch (2014-2015)
- 2014: Ethereum held a successful crowdsale (ICO), raising over $18 million—a significant sum for the time. The ICO drew attention from a growing community of blockchain enthusiasts and investors. It was also one of the first ICOs to offer a blockchain-based platform for decentralized applications.
- July 30, 2015: After over a year of development, Ethereum officially launched with the first version of the Ethereum network called “Frontier”. At this point, the Ethereum blockchain was live, and the native cryptocurrency, Ether (ETH), began to be mined and used to pay for transaction fees and computational work.
3. The DAO and Hard Fork (2016)
- 2016: Ethereum experienced one of the most significant events in its history—the DAO hack. The DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization) was a decentralized investment fund built on the Ethereum network, and it raised over $150 million in ETH. However, a vulnerability in its smart contract code was exploited by an attacker, leading to the theft of approximately $50 million worth of ETH.
- Hard Fork Controversy: To reverse the effects of the hack, the Ethereum community decided to perform a controversial hard fork, splitting the Ethereum blockchain into two:
- Ethereum (ETH): The new chain that reversed the hack and refunded investors.
- Ethereum Classic (ETC): The original chain that did not reverse the hack, maintaining the immutability of the blockchain.
4. Continuous Growth and Ethereum’s Ecosystem (2017-2020)
- 2017: Ethereum gained significant attention during the ICO boom of 2017, with thousands of new tokens and projects being launched on the Ethereum network using the ERC-20 token standard. This brought massive growth to the Ethereum ecosystem and led to increased demand for ETH. During this period, Ethereum also saw a surge in decentralized applications (dApps), with applications for decentralized finance (DeFi), gaming, and more being built on the platform.
- 2017-2018: Ethereum became the go-to platform for launching Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) and tokens, leading to a rapid increase in Ethereum’s adoption and market value. However, it also faced growing concerns about scalability and high transaction fees due to network congestion.
- 2018: The Ethereum community started discussing Ethereum 2.0, a major upgrade that would address scalability issues and shift the network from a Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism to a more energy-efficient Proof-of-Stake (PoS) mechanism.
5. Ethereum 2.0 and the Future (2020-Present)
- 2020: The Ethereum 2.0 upgrade officially began with the launch of the Beacon Chain in December 2020. This marked the start of Ethereum’s transition to Proof-of-Stake (PoS), which aims to improve scalability, reduce energy consumption, and enhance the security of the network. Ethereum 2.0 will eventually replace the current Proof-of-Work system to address high gas fees and network congestion.
- 2021: Ethereum saw a major resurgence in both price and use cases, largely driven by the explosion of decentralized finance (DeFi) and the rise of non-fungible tokens (NFTs), both of which primarily use the Ethereum blockchain. ETH reached all-time highs, and its role as the leading platform for smart contracts and decentralized applications solidified.
- 2021-2022: Ethereum faced significant competition from newer blockchain platforms like Solana, Binance Smart Chain, and Cardano, all of which promised lower transaction fees and faster speeds. However, Ethereum remains the dominant platform for DeFi applications, NFTs, and smart contracts.
- 2023 and Beyond: Ethereum continued to evolve, with Ethereum 2.0 (also known as The Merge) officially switching to Proof-of-Stake in September 2022, a major milestone aimed at making the network more scalable, secure, and sustainable. Ethereum’s future looks promising as it continues to be the foundational blockchain for decentralized applications, NFTs, and smart contracts.
Key Milestones in Ethereum’s History
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 2013 | Vitalik publishes the Ethereum whitepapEr. |
| 2014 | Ethereum ICO raises $18 million. Ethereum project officially begins. |
| 2015 | Ethereum launches with the Frontier network. |
| 2016 | The DAO hack leads to the Ethereum hard fork, splitting Ethereum and Ethereum Classic (ETC). |
| 2017 | Ethereum becomes the platform for ICOs, tokens, and dApps. |
| 2018 | Ethereum begins work on Ethereum 2.0 to move to Proof-of-Stake. |
| 2020 | Ethereum 2.0’s Beacon Chain is launched, starting the PoS transition. |
| 2021 | Ethereum’s price hits new highs amid DeFi and NFT boom. |
| 2022 | Ethereum completes the Merge, transitioning from Proof-of-Work to Proof-of-Stake. |
| 2023 and Beyond | Ethereum focuses on scaling solutions like Layer 2 (e.g., Optimism, Arbitrum) and further upgrades. |
Ways to make money with Ethereum
There are several ways to make money with Ethereum Coin (ETH) in the cryptocurrency ecosystem. These methods vary in terms of risk, technical knowledge required, and involvement, but they all offer opportunities for profit. Here are the most common ways to make money with Ethereum:

1. Buying and Holding (HODLing)
- How it Works: This is one of the simplest ways to make money with Ethereum. It involves buying ETH at a certain price and holding it for an extended period, hoping its value will increase over time. Many people use this strategy during bull markets when they believe the price of ETH will rise.
- Risk: The price of ETH is volatile, and you could potentially lose money if the market moves against you.
- Potential Earnings: Profit depends on the market timing—if ETH appreciates significantly, your returns could be substantial.
2. Staking ETH (Ethereum 2.0)
- How it Works: Ethereum 2.0 introduced a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) mechanism, allowing ETH holders to stake their coins in the network to help secure it and validate transactions. you need a minimum of 32 ETH or you can join a staking pool with smaller amounts.
- Risk: Staked ETH can be locked up for long periods, and there is a risk of losing some or all of your staked ETH due to validator misbehavior.
- Potential Earnings: Staking rewards vary but typically range from 4% to 10% annually depending on network conditions.
3. Yield Farming (DeFi)
- How it Works: Yield farming involves using your Ethereum (ETH) to provide liquidity to decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms in exchange for interest or rewards. By locking up ETH in liquidity pools, you can earn returns in the form of additional ETH or other tokens.
- Risk: Yield farming can be risky due to potential smart contract vulnerabilities, impermanent loss (loss from providing liquidity), and platform risks.
- Potential Earnings: Returns can vary widely but can sometimes reach double digits (20% or more annually), depending on the platform and the assets you’re providing liquidity for.
4. Ethereum Mining (Proof-of-Work)
- How it Works: Ethereum originally used the Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, which required miners to solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions. In return for their work, miners earned ETH as a reward. However, since Ethereum transitioned to Proof-of-Stake in 2022 (Ethereum 2.0), traditional PoW mining is no longer available on the Ethereum network.
- Risk: Ethereum mining was energy-intensive, and the transition to PoS has made mining obsolete for ETH.
- Potential Earnings: Miners could previously earn a substantial amount of ETH, but with Ethereum 2.0’s move to PoS, this opportunity has largely disappeared for ETH holders.
5. Trading ETH (Active Trading)
- How it Works: Active trading involves buying and selling ETH at different prices to take advantage of short-term price fluctuations. Traders often use strategies like day trading, swing trading, and technical analysis to predict price movements and make profits.
- Risk: Trading involves significant risk, as cryptocurrency prices are volatile and unpredictable. It requires skill, knowledge, and attention to market trends.
- Potential Earnings: Profits depend on your trading skills and market conditions, but experienced traders can generate significant returns. However, losses are also possible.
6. Earning ETH through Lending (DeFi Lending)
- How it Works: DeFi lending platforms like Aave, Compound, and MakerDAO allow you to lend your ETH to others in exchange for interest. By lending your Ethereum, you can earn passive income on your holdings.
- Risk: There is always the risk of borrowers defaulting, smart contract vulnerabilities, and platform insolvency.
- Potential Earnings: The interest rates vary, but typically you can expect to earn between 3% to 10% annually, depending on demand and the lending platform.
7. Earning ETH from Faucets
- How it Works: Ethereum faucets are websites that give out small amounts of ETH for free, usually in exchange for completing simple tasks like viewing ads or solving captchas. While the amounts are minimal, it’s an easy, no-investment way to start collecting ETH.
- Risk: Faucets offer very small amounts of ETH, so it’s not a significant way to make money. It can be time-consuming for little reward.
- Potential Earnings: Generally, earnings are small—usually only a fraction of an ETH per day or week.
8. Participating in Initial Coin Offerings
- How it Works: Many new projects and tokens are launched on the Ethereum blockchain. By participating in an ICO or Token Sale, you can buy new tokens at a low price and potentially sell them later at a profit if the project becomes successful.
- Risk: ICOs can be very risky, as many projects fail, are scams, or face regulatory issues. Proper research and caution are required before investing.
- Potential Earnings: If you invest in a successful project, the returns can be significant. However, it is highly speculative and risky.
9. Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
- How it Works: Ethereum is the primary blockchain for creating and trading Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)—unique digital assets that represent ownership of things like art, music, and virtual real estate. You can either create and sell your own NFTs or buy NFTs with the expectation that their value will increase over time.
- Risk: The NFT market can be highly speculative, and prices can be volatile. Not all NFTs will appreciate, and there’s always the possibility of losing your investment.
- Potential Earnings: If you buy or create NFTs that become highly sought after, you could earn substantial profits. However, the NFT space can be unpredictable.
10. Ethereum Airdrops
- How it Works: An airdrop is when a project distributes free tokens (often based on Ethereum) to holders of a specific cryptocurrency, including ETH. Some projects do airdrops to increase awareness or to reward users for being early adopters.
- Risk: Airdrops are generally free, but the tokens you receive might not have much value. Also, you might need to meet certain conditions or be cautious of scams.
- Potential Earnings: Airdrops can be small, but occasionally, some tokens may gain significant value, leading to profits.
How to Invest in Ethereum Coin
Investing in Ethereum Coin (ETH) involves several steps, from setting up an account on a cryptocurrency exchange to safely storing your ETH. Below is a step-by-step guide to help you get started with investing in Ethereum:
1. Choose a Cryptocurrency Exchange
To buy Ethereum, you’ll need to sign up on a cryptocurrency exchange. Some of the most popular exchanges where you can buy, sell, and trade ETH include:
- Coinbase: Known for its user-friendly interface and security features, ideal for beginners.
- Binance: A larger platform with a wide range of cryptocurrencies, including ETH.
- Kraken: A trusted exchange with robust security features and a wide range of assets.
- Gemini: Offers both a user-friendly platform and advanced trading options.
- eToro: Allows users to buy ETH and other cryptocurrencies with traditional payment methods.
2. Create and Verify Your Account
- Sign Up: After choosing an exchange, you’ll need to create an account by providing your personal details such as name, email address, and phone number.
- Identity Verification: Most exchanges require users to go through a Know Your Customer (KYC) process, which typically involves submitting identification documents (like a passport or driver’s license) to verify your identity. This is a standard process to comply with financial regulations.
3. Deposit Funds into Your Account
Before you can buy Ethereum, you’ll need to deposit money into your exchange account. Common ways to fund your account include:
- Bank Transfer: Linking a bank account for a direct transfer of funds.
- Credit/Debit Card: Many exchanges accept credit and debit cards for purchasing ETH, though they may charge higher fees.
- Cryptocurrency Transfer: If you already own other cryptocurrencies, you can transfer them to the exchange and trade for Ethereum.
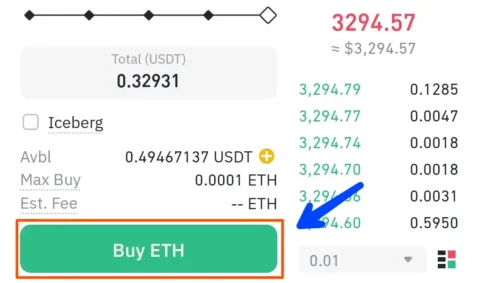
4. Place a Buy Order for Ethereum (ETH)
Once your account is funded, you can place a buy order for Ethereum:
- Market Order: It buys ETH at the current market price.
- Limit Order: You specify a price at which you want to buy Ethereum. The order will only be executed if the price hits your specified target.
- Stop-Loss Order: This type of order helps limit your losses by automatically selling your ETH if the price falls below a certain point.
5. Store Your Ethereum Safely
After purchasing Ethereum, you need to decide where to store it. There are two main options for securely holding your ETH:
- Exchange Wallet: This is where your ETH is stored on the exchange. While convenient, it is not the most secure option because the exchange can be hacked or go out of business.
- Private Wallets:
- Hot Wallets: These are software wallets connected to the internet (e.g., MetaMask, Trust Wallet). They are user-friendly but are susceptible to online hacking attempts.
- Cold Wallets: These are offline hardware wallets (e.g., Ledger, Trezor), which are more secure as they store your private keys offline, making them less vulnerable to cyberattacks.
6. Monitor Your Investment
After you’ve bought ETH and secured it, you should regularly monitor its price, performance, and market trends. Tools like CoinMarketCap and CoinGecko can help you track Ethereum’s price in real time.
7. Consider Long-Term vs. Short-Term Investment
- Long-Term Hold (HODL): Many investors choose to hold Ethereum for the long term, betting on its future growth as the blockchain evolves and adoption increases. You may want to stake ETH (in Ethereum 2.0) for additional rewards.
- Active Trading: If you prefer to take advantage of short-term price movements, you can trade ETH. However, this requires a good understanding of technical analysis and market timing.
8. Diversify Your Portfolio
Although Ethereum is a strong investment, diversification is important in any investment strategy. Consider balancing your ETH holdings with other cryptocurrencies or traditional investments to reduce risk.
9. Stay Informed
The cryptocurrency market can be volatile and unpredictable. Stay updated on news, Ethereum upgrades (like Ethereum 2.0), regulations, and developments in the DeFi and NFT sectors that might impact the price of ETH.
10. Tax Considerations
In many countries, cryptocurrency gains are subject to taxes. Make sure you understand the tax implications of investing in Ethereum, including capital gains tax. Consider consulting with a tax professional if you’re unsure.
FAQs –
Q 1. What is the price of Ethereum right now
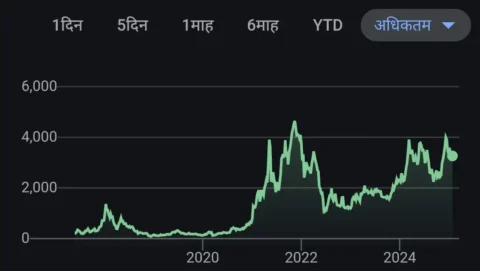
Answer – Currently the price of Ethereum is 3269 USDT if you want to check the real data so I recommend checking a reliable cryptocurrency tracking platform like CoinMarketCap, CoinGecko, or your preferred exchange for the latest price of Ethereum (ETH).
Q 2. How much will the price of Ethereum coin increase?
Answer – Predicting the exact future price of Ethereum (ETH) is highly uncertain and speculative. However, based on current trends and factors, there are some key influences that could drive its price higher:
- Ethereum 2.0 Upgrade: The transition to Ethereum 2.0 (Proof-of-Stake) is expected to improve scalability, lower fees, and make the network more sustainable. This could lead to increased adoption and demand for ETH, which may drive the price higher.
- Growth of DeFi and NFTs: As Ethereum remains the dominant platform for decentralized finance (DeFi) applications and non-fungible tokens (NFTs), continued growth in these sectors could fuel increased demand for ETH.
- Institutional Adoption: More institutional investors and large companies are getting involved in Ethereum, which could lead to greater demand and higher prices.
- Market Sentiment: The price of Ethereum, like other cryptocurrencies, will continue to be influenced by the overall sentiment in the crypto market. A bullish market for Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies could also benefit ETH.
Some analysts have speculated that Ethereum could see significant price appreciation in the coming years, with some predicting it could reach anywhere between $5,000 to $10,000 per ETH over the next 1-3 years, but these predictions are subject to market volatility and unforeseen factors.
As with any cryptocurrency, it is important to keep in mind that the price of Ethereum is highly volatile, and investing in it carries substantial risk. Always conduct thorough research before investing.
Conclusion –
Ethereum (ETH) has established itself as a cornerstone of the cryptocurrency and blockchain ecosystem, providing a decentralized platform for smart contracts, decentralized applications (dApps), and decentralized finance (DeFi). With its ongoing upgrades, including the transition to Ethereum 2.0, Ethereum aims to address scalability, security, and energy efficiency, further cementing its role in the future of blockchain technology.
As Ethereum continues to evolve, it holds great potential for investors, developers, and users alike, particularly with its integral role in the booming NFT market, DeFi applications, and the growing interest from institutional investors. While there are risks associated with investing in Ethereum, including market volatility and regulatory uncertainties, its widespread adoption and continued development make it one of the most promising cryptocurrencies.
In summary, Ethereum presents exciting opportunities for those interested in the blockchain and cryptocurrency space. However, as with any investment, it’s crucial to stay informed, understand the risks, and carefully consider your financial goals before making decisions related to Ethereum.